Challenges in short-stem total hip arthroplasty

Short-stem total hip arthroplasty (THA) is a surgical approach that involves using shorter femoral stems compared to traditional hip replacement procedures. While short-stem THA offers certain advantages, it also presents specific challenges. Here are some of the challenges associated with short-stem total hip arthroplasty:
Limited Fixation Area: Short-stem implants have a reduced surface area for fixation in the femoral canal compared to longer stems. This limited area may affect the stability and long-term fixation of the implant, potentially leading to concerns about implant loosening over time.
Limited Load Transfer: The shorter length of the stem may impact load transfer through the femur. Achieving optimal load distribution is crucial for the longevity and success of the implant. Improper load transfer could contribute to issues such as stress shielding or uneven distribution, potentially affecting bone remodeling.
Limited Modularity: Short-stem designs may have limited modularity compared to traditional stems. Modularity allows surgeons to adjust the length and offset of the stem during surgery. Limited modularity might make it challenging to achieve an optimal fit for each patient.
Surgical Learning Curve: Implementing short-stem THA requires a learning curve for surgeons. Mastery of the specific techniques and nuances associated with short-stem procedures is crucial for achieving good outcomes. Surgeons may need training to become proficient in the use of short-stem implants.
Patient Selection: The success of short-stem THA may be influenced by appropriate patient selection. Factors such as patient anatomy, bone quality, and individual variability need to be carefully considered to ensure that short-stem implants are suitable for a particular patient.
Limited Long-Term Data: While short-stem THA has shown promising early and mid-term results, there may be a limited amount of long-term data available. Long-term follow-up studies are essential to assess the durability, survivorship, and potential complications associated with short-stem implants over an extended period.
Implant Design Variability: Different manufacturers may produce short-stem implants with varying designs and features. The lack of standardization in design can make it challenging for surgeons to choose the most appropriate implant for a specific patient.
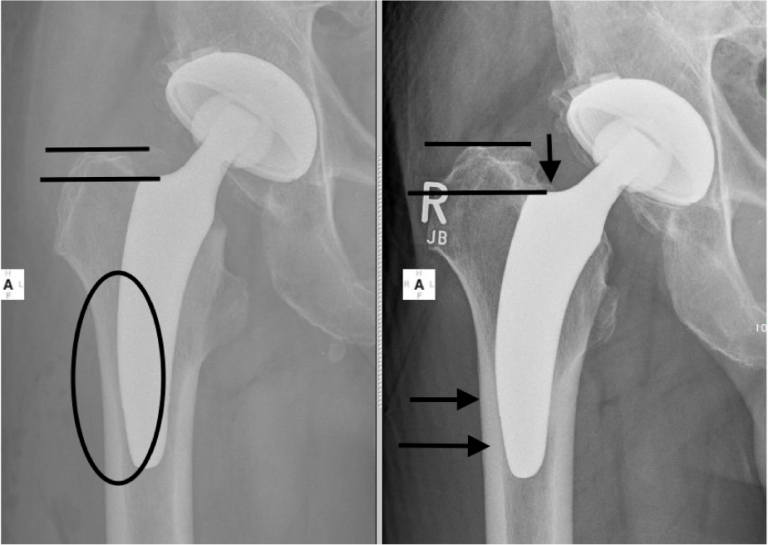
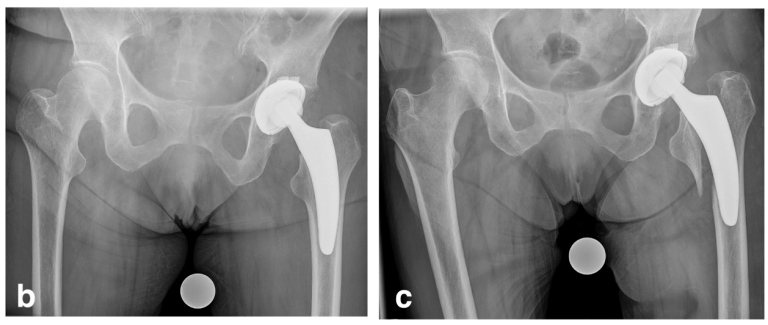
Short stems: Is it really the easy way?
Long-Term Outcomes and Follow-Up Studies
While short-stem total hip arthroplasty (THA) has demonstrated promising outcomes in the short term, the long-term performance of these implants remains a subject of ongoing research. Longitudinal studies and follow-up assessments are essential to comprehensively evaluate the durability, stability, and functionality of short-stem implants over extended periods.
Research initiatives are continually exploring the longevity of short-stem THA, assessing factors such as implant survivorship, complications, and patient-reported outcomes. Long-term data contribute valuable insights into the effectiveness and reliability of short-stem implants, aiding surgeons in refining patient selection criteria and enhancing overall surgical outcomes.
Comparative Effectiveness Studies
Comparative effectiveness studies play a crucial role in assessing the relative merits of short-stem THA in comparison to traditional long-stem implants. Evaluating factors such as implant stability, bone preservation, postoperative pain, and patient satisfaction allows surgeons and researchers to make informed decisions regarding the most appropriate implant for specific patient populations.
These studies consider not only the clinical outcomes but also economic factors, resource utilization, and healthcare costs associated with different implant options. Comparative effectiveness research provides valuable evidence to guide evidence-based decision-making and further refines the understanding of the role of short-stem THA in the orthopedic landscape.
Surgeon Learning Curve and Training
The adoption of short-stem THA may require surgeons to navigate a learning curve, as the surgical techniques and considerations differ from those associated with traditional long-stem implants. Training programs, hands-on workshops, and mentorship opportunities are essential for surgeons to develop proficiency in short-stem procedures.
As with any surgical innovation, ensuring that surgeons are adequately trained and confident in their skills is paramount to optimizing patient outcomes. Ongoing education and collaboration within the orthopedic community contribute to the dissemination of best practices and the refinement of surgical techniques associated with short-stem THA.
Regulatory Approval and Guidelines
Regulatory approval and adherence to established guidelines are critical considerations in the widespread adoption of short-stem THA. Regulatory bodies, such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and equivalent organizations globally, play a pivotal role in evaluating the safety and efficacy of new implant designs.
Guidelines from professional orthopedic associations provide frameworks for the responsible and evidence-based incorporation of short-stem THA into clinical practice. These guidelines encompass considerations such as patient selection criteria, surgical techniques, and postoperative care, ensuring standardized practices that prioritize patient safety and positive outcomes.
Addressing Potential Concerns and Controversies
The adoption of innovative technologies, including short-stem THA, may be accompanied by concerns and controversies within the orthopedic community. Addressing these concerns requires ongoing research, open dialogue, and collaborative efforts among surgeons, researchers, and regulatory bodies.
Common concerns may include the potential for increased periprosthetic fractures, implant subsidence, or challenges in achieving optimal fit and stability. Proactive measures, such as refining implant designs, developing standardized protocols, and conducting rigorous clinical studies, contribute to addressing these concerns and building confidence in the safety and efficacy of short-stem THA.
As short-stem THA continues to evolve, addressing challenges and controversies is integral to refining the approach and ensuring its continued success.
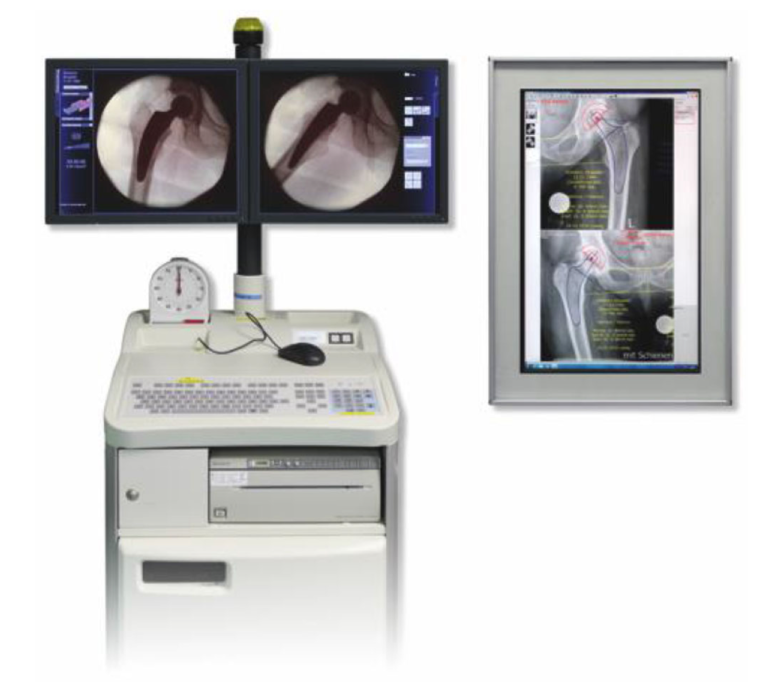
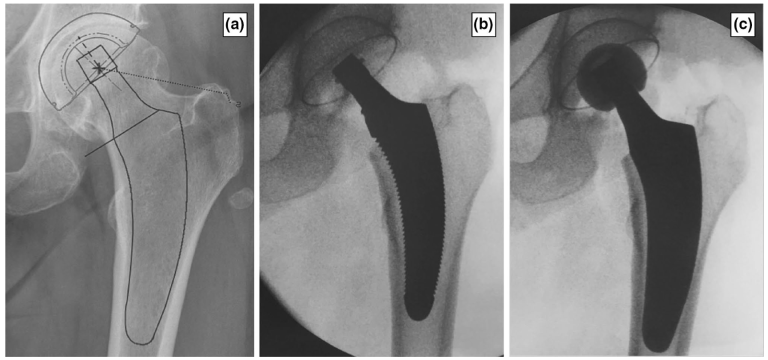
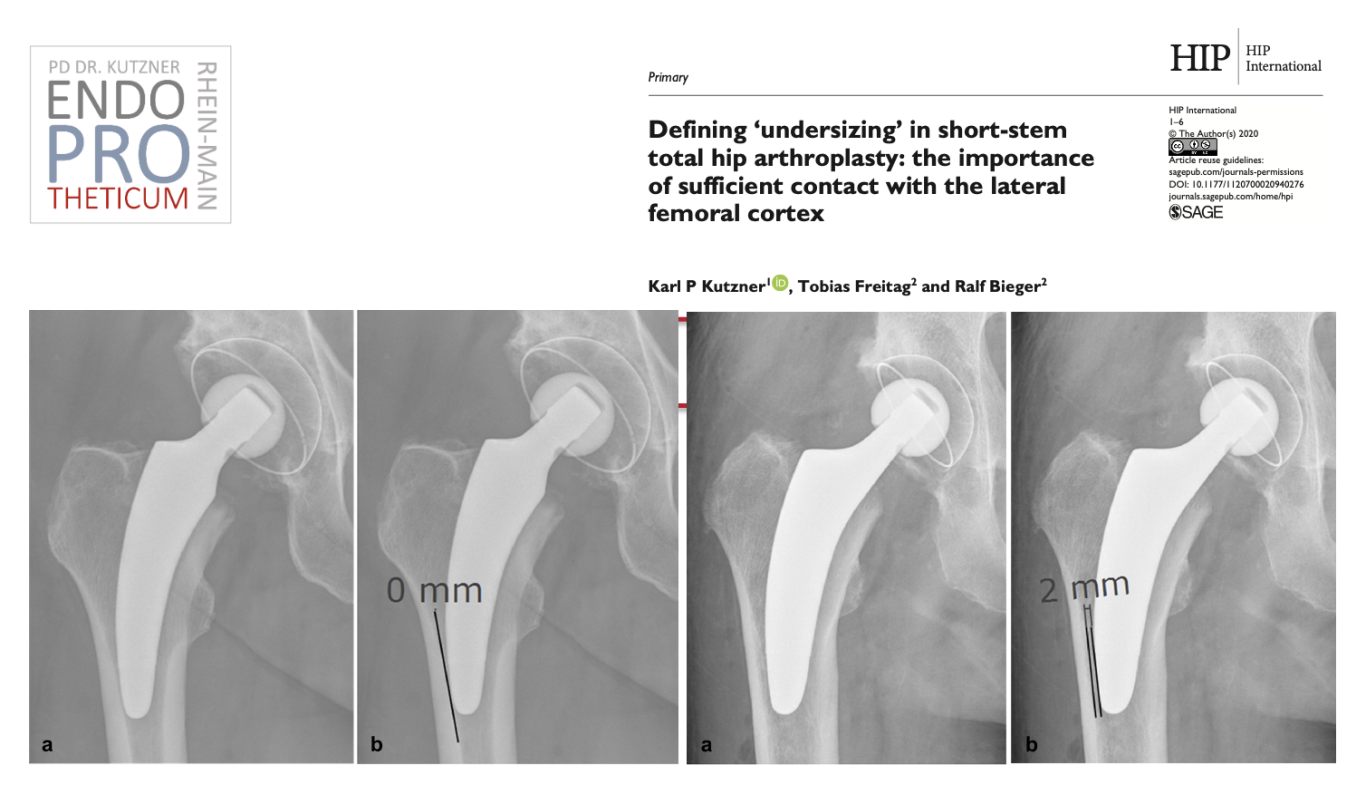

Due to the individualized approach regarding stem positioning in short-stem total hip arthroplasty, intraoperative radiography is mandatory. It helps to determine the alignment, detects undersizing, allows adjustments and secures the optimal outcome.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.