Surgical techniques in short-stem total hip arthroplasty

Short-stem total hip arthroplasty is closely associated with minimally invasive surgical techniques. The use of smaller incisions aims to reduce soft tissue disruption, leading to decreased postoperative pain, accelerated recovery, and improved patient satisfaction. Minimally invasive techniques associated with short-stem THA contribute to shorter hospital stays, and faster overall recovery.
The adoption of short-stem THA techniques requires a learning curve for surgeons. Mastery of the technique and familiarity with implant-specific considerations are essential for success.
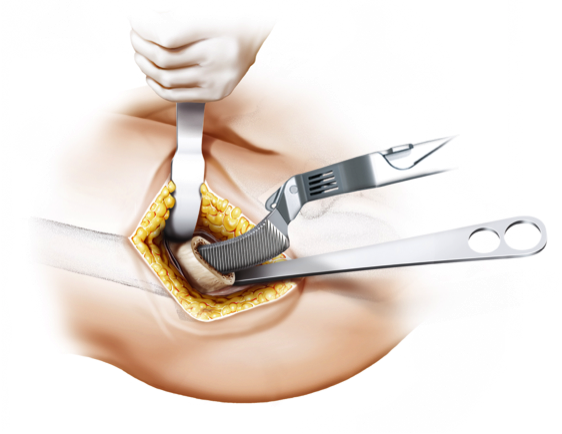
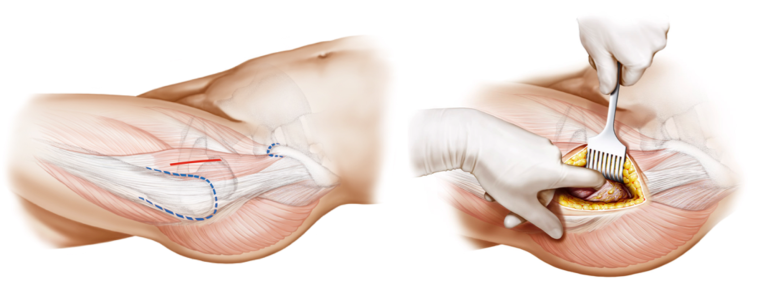
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Short-stem total hip arthroplasty (THA) is often associated with minimally invasive surgical (MIS) techniques, representing a departure from the more traditional, larger-incision approaches. Minimally invasive surgery aims to reduce soft tissue disruption, decrease postoperative pain, accelerate recovery, and enhance overall patient satisfaction.
The use of smaller incisions in MIS for short-stem THA requires specialized training and expertise on the part of the surgeon. This approach allows for a more tissue-sparing procedure, potentially leading to shorter hospital stays and quicker rehabilitation for the patient. However, the adoption of minimally invasive techniques should be balanced with ensuring proper exposure, component positioning, and achieving optimal outcomes.
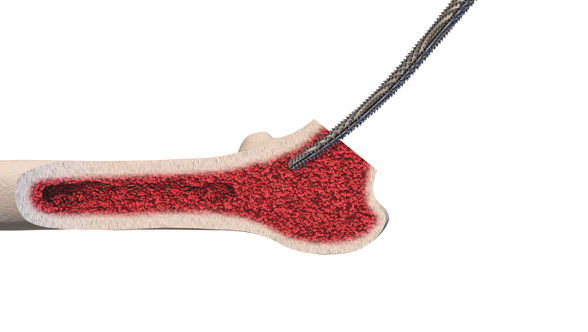
Femoral Neck Preservation Techniques
Preservation of the femoral neck is a key consideration in short-stem THA, and various techniques aim to achieve this goal. The femoral neck is critical for maintaining the biomechanics of the hip joint and ensuring proper load transfer. Preserving the natural anatomy of the femoral neck is particularly relevant in short-stem designs, where stability and functionality depend on maintaining these anatomical features.
Calcar-guided short stems, for example, are designed to preserve the calcar region of the femoral neck, contributing to enhanced stability and load distribution. Techniques that prioritize femoral neck preservation not only aim to replicate the natural biomechanics of the hip joint but also play a role in improving long-term outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
Customization and Personalization in Short-Stem Surgery
One of the notable advantages of short-stem THA is the ability to customize and personalize the surgical approach based on individual patient anatomy. Short-stem implants often come with modular options, allowing surgeons to choose components that closely match the patient's unique femoral morphology.
Customization extends beyond implant selection and involves tailoring the surgical technique to the patient's specific needs. Computer-assisted navigation and robotic surgery are emerging technologies that offer additional precision in implant placement, further enhancing the level of customization in short-stem THA.
Tips for Surgeon Proficiency
Proficiency in short-stem THA requires a learning curve for surgeons, as the techniques and considerations differ from those associated with traditional long-stem implants. To optimize outcomes and minimize potential complications, surgeons adopting short-stem THA should consider the following:
- Ongoing Education: Stay abreast of the latest developments in short-stem technology through continued medical education, training courses, and participation in conferences.
- Mentorship: Seek mentorship from experienced surgeons who have a proven track record in short-stem THA to benefit from their insights and guidance.
- Hands-on Training: Participate in hands-on workshops and cadaveric labs to gain practical experience and refine surgical skills specific to short-stem procedures.
- Patient Selection: Carefully select patients based on individual factors such as age, bone quality, and anatomical considerations to ensure the suitability of short-stem implants.
The proficiency of the surgeon in short-stem THA is instrumental in achieving optimal outcomes, and ongoing advancements in surgical techniques will continue to refine the approach.
Soft-tissue and bone preserving short-stem THA
Tips and Tricks with the optimys stem

Successful implementation of short-stem THA requires surgeon expertise and familiarity with the specific challenges and advantages associated with these implants. Adequate training and continuous education are essential for optimizing outcomes.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.