Outcomes in short-stem total hip arthroplasty

Summarizing the scientific literature on short-stem total hip arthroplasty (THA) involves synthesizing a vast body of research that spans various aspects of this surgical technique. Below is a concise overview of key findings and trends derived from scientific literature. You will find the corresponding literature in the "literature" section.
Scientific findings in short-stem THA
Clinical Outcomes
• Patient Satisfaction: Numerous studies report high levels of patient satisfaction following short-stem THA. Patients often experience less postoperative pain, quicker recovery, and improved quality of life compared to traditional long-stem implants.
• Functional Outcomes: Short-stem THA has been associated with favorable functional outcomes, with many patients achieving or surpassing preoperative levels of activity and range of motion.
Bone Preservation
• Metaphyseal Fixation: Short-stem implants, designed to engage the metaphyseal region of the femur, aim to preserve bone stock. Studies suggest that this approach may reduce the risk of stress shielding and facilitate future revisions.
• Bone Remodeling: Research indicates that short-stem THA may result in less bone loss compared to traditional stems, contributing to improved long-term outcomes and potential advantages in younger, more active patient populations.
Complications and Revision Rates
• Lower Dislocation Rates: Short-stem THA is often associated with lower dislocation rates compared to traditional implants. Enhanced stability, coupled with proper surgical technique, contributes to reduced risk of dislocation.
• Low Revision Rates: Studies suggest that short-stem implants demonstrate low revision rates, indicating the durability and success of the procedure. However, long-term data are essential to fully assess the implant's longevity.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
• Reduced Soft Tissue Disruption: Short-stem THA is often performed using minimally invasive techniques, resulting in smaller incisions and reduced soft tissue disruption. This approach is linked to faster recovery, shorter hospital stays, and improved postoperative outcomes.
Patient Selection and Customization:
• Individualized Approaches: Advances in imaging technologies, including 3D printing, allow for the customization of short-stem implants based on individual patient anatomy. Tailoring implants to specific anatomical variations may contribute to improved outcomes.
• Consideration for Younger Patients: Short-stem THA is often considered for younger and more active patients, emphasizing the preservation of bone for potential future revisions.
Technological Advancements:
• Robotics and Navigation: The integration of robotics and computer-assisted navigation systems has gained prominence in short-stem THA. These technologies enhance precision in implant placement, potentially reducing the learning curve for surgeons.
• Advanced Imaging: Three-dimensional (3D) imaging and virtual reality (VR) are increasingly utilized for preoperative planning, allowing surgeons to visualize anatomical structures and optimize implant positioning.
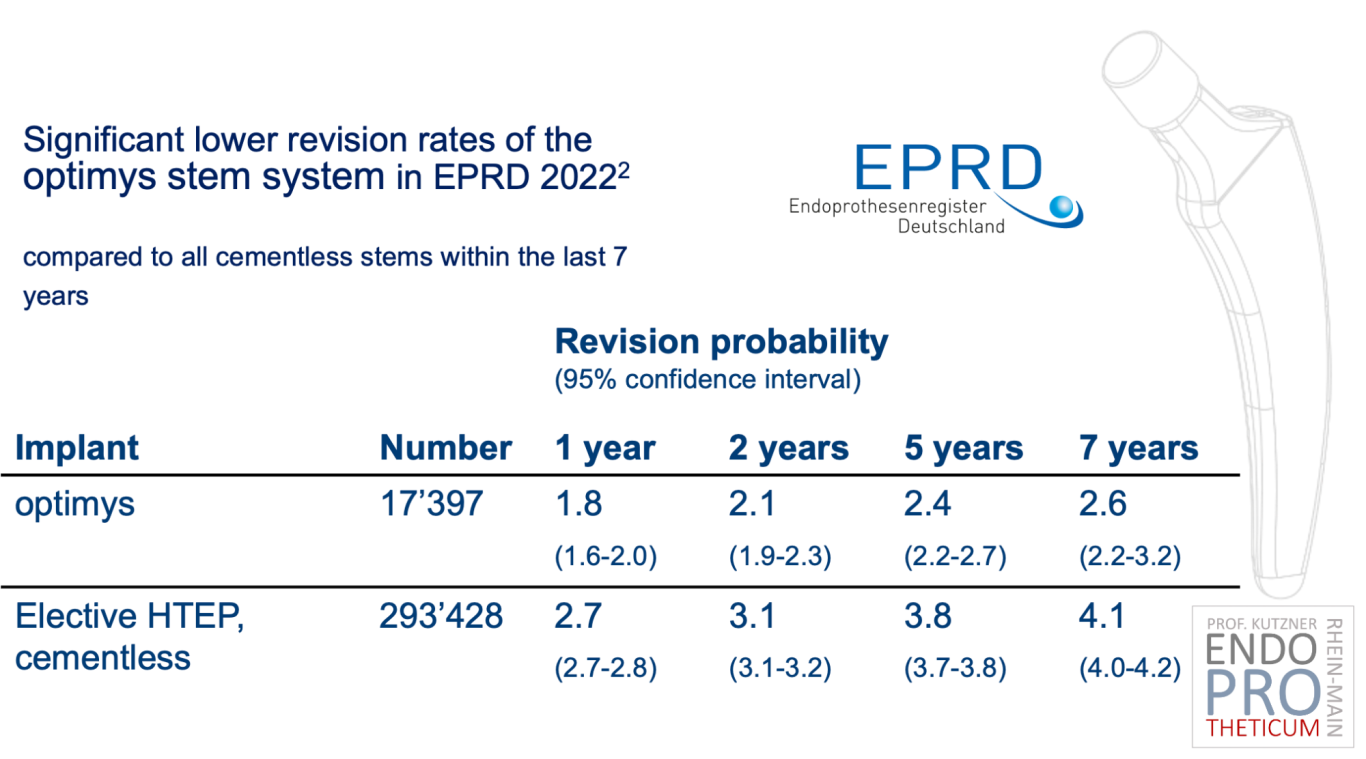
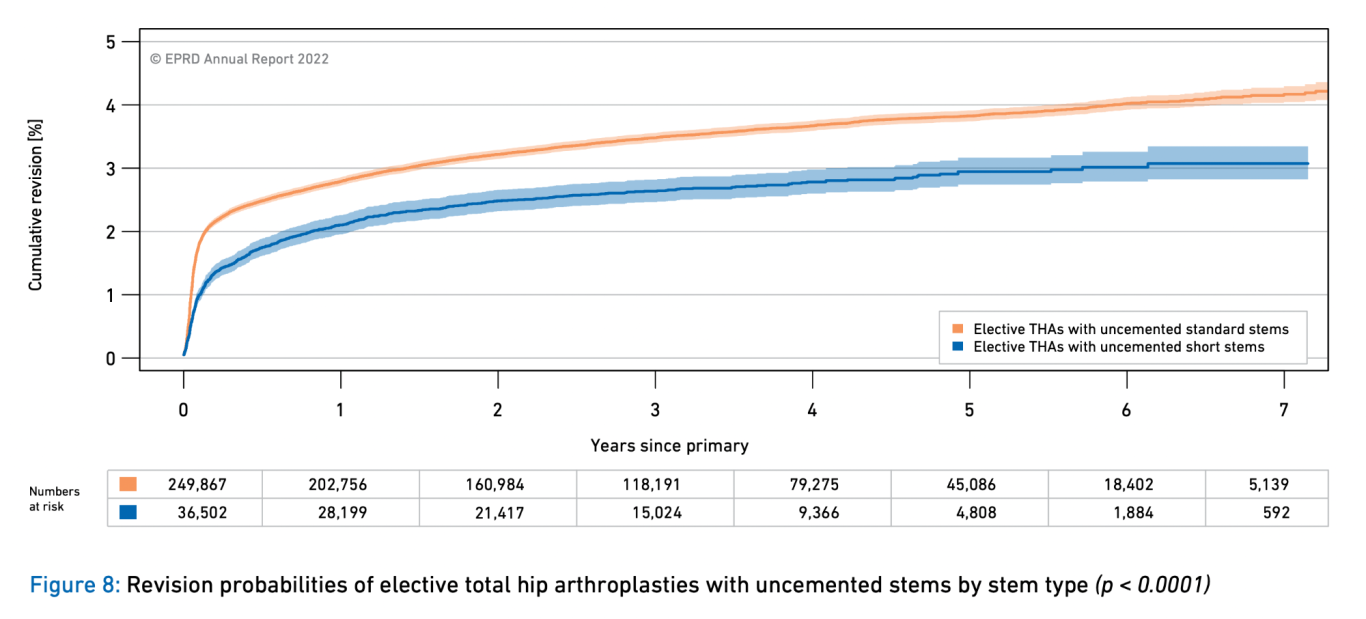
From primary to secondary stability in short-stem THA

Calcar-guided short stems, such as the optimys stem, are the most successful stems in terms of survival and complications at 8 years in most registries worldwide. I believe it is the future of THA.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.