Short-stem total hip arthroplasty - an overview
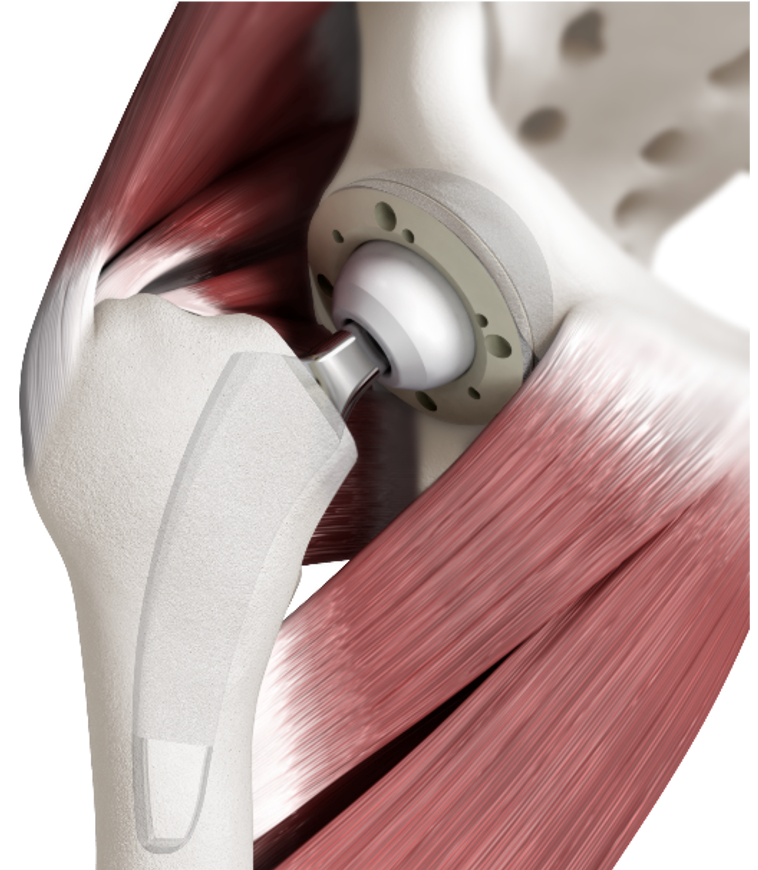
Short-stem total hip arthroplasty (THA) is characterized by the use of femoral components with a reduced length compared to traditional implants. These stems typically engage the metaphysis and may preserve more of the patient's natural femoral anatomy. The design principles of short stems aim to achieve stability, load transfer, and bone preservation, addressing concerns associated with long-stem implants.
The concept of short-stem THA emerged as an evolution in hip replacement surgery, aiming to address certain challenges associated with traditional, longer stem designs. The history of short stems in THA can be traced back several decades, and the development of these implants reflects ongoing efforts to improve surgical techniques, reduce invasiveness, and optimize patient outcomes. Here is a general overview of the historical progression of short stems in THA:
Early Hip Arthroplasty:
The first hip arthroplasties were performed in the mid-20th century using long-stem femoral components. While these early procedures were groundbreaking, concerns arose regarding the impact of long stems on bone preservation, stress shielding, and the potential for complications.
Evolution of Hip Implant Designs:
Over the years, hip implant designs underwent various modifications to address issues related to bone preservation and implant stability. Advances in materials, such as the transition from metal-on-metal to metal-on-polyethylene and ceramic-on-ceramic bearing surfaces, played a role in improving implant durability.
Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS):
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, there was a growing emphasis on minimally invasive surgical techniques. Short-stem implants became part of this trend, as they allowed for smaller incisions and reduced soft tissue disruption compared to traditional long-stem designs.
Introduction of Short Stems:
The first short stems were introduced in the 1990s as alternatives to traditional stems. These early designs were often metaphyseal or neck-preserving stems, aiming to reduce the impact on the femoral canal while providing stability.
Anatomic Considerations:
As understanding of hip anatomy deepened, short stems began to incorporate more anatomic features. Surgeons sought to develop stems that closely mimicked the natural shape and orientation of the femur, including the calcar, to enhance stability and load transfer.
Calcar-Guided Designs:
Calcar-guided short-stem designs, which focus on preserving the femoral calcar, gained attention as a way to further improve outcomes. These designs aim to maintain bone stock and provide a more anatomically congruent implant.
Advancements in Materials and Manufacturing:
Advances in metallurgy, manufacturing techniques, and imaging technology have contributed to the development of newer short-stem designs. Modern materials and manufacturing methods allow for more precise customization and improved implant performance.
Clinical Studies and Outcomes:
Over time, numerous clinical studies have been conducted to evaluate the safety, efficacy, and long-term outcomes of short-stem THA. These studies have contributed to the refinement of surgical techniques and implant designs.
Current Status:
Short-stem implants have become established options in hip replacement surgery. Surgeons may choose from various designs based on patient factors, surgical preferences, and implant characteristics.
Modern achievements in total hip arthroplasty
When seeking a specialist in short-stem THA, consider factors such as the surgeon's experience, patient outcomes, research contributions, and reputation in the orthopedic community. Additionally, consulting with your primary care physician or local orthopedic surgeon can be a valuable step in finding a specialist who meets your specific needs.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.